General health encompasses the overall condition of an individual’s physical, mental, and social well-being. It is not merely the absence of disease or infirmity but a balanced state that allows a person to function effectively in daily life. Maintaining good health involves attention to a variety of factors, including diet, exercise, sleep, and preventative care. These aspects contribute to the resilience of the body and mind, and support long-term wellbeing.
Components of Physical Health
In contemporary society, access to accurate health news is essential for individuals seeking to make informed decisions about their lifestyle and well-being. Reliable information can help clarify misconceptions and guide choices regarding nutrition, physical activity, and medical interventions.
Nutrition and Diet
Nutrition plays a central role in general health. A balanced diet provides the body with essential nutrients such as proteins, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Each nutrient has a specific function; for example, proteins support tissue growth and repair, while carbohydrates are the primary source of energy.
Dietary guidelines recommend a variety of foods to ensure adequate nutrient intake. Fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins are often emphasised because they supply fibre, antioxidants, and other beneficial compounds. Reducing consumption of processed foods, high sugar items, and excessive salt can lower the risk of chronic conditions such as heart disease and type 2 diabetes.

Physical Activity
Regular physical activity contributes to the maintenance of a healthy weight, supports cardiovascular fitness, and enhances muscular strength. Exercise also influences metabolic processes and can improve mental well-being. Health authorities commonly suggest at least 150 minutes of moderate intensity activity per week for adults, alongside muscle-strengthening activities on two or more days per week.
Different types of exercise yield distinct benefits. Aerobic activities such as walking, cycling, or swimming enhance heart and lung function, while resistance training improves strength and bone density. Flexibility exercises support joint mobility and can reduce the risk of injury.
Sleep and Rest
Adequate sleep is essential for restoration and overall health. During sleep, the body undergoes important processes including tissue repair, memory consolidation, and regulation of hormones. Adults typically require between seven and nine hours of sleep each night, although individual needs can vary.
Chronic sleep deprivation has been linked to a range of health issues, including impaired cognitive function, weakened immunity, and increased risk of chronic diseases. Establishing regular sleep patterns and creating a restful environment can help support restorative sleep.
Mental and Emotional Well-being

Stress Management
Stress is a natural response to challenging situations. However, prolonged or unmanaged stress can negatively affect both mental and physical health. It is associated with symptoms such as anxiety, irritability, headaches, and disturbances in sleep.
Effective stress management strategies may include mindfulness techniques, regular exercise, and engaging in hobbies. Social support from friends, family, or professional counsellors can also play a significant role in coping with stress.
Emotional Health
Emotional health refers to the ability to understand and manage emotions. It influences how individuals react to life situations, relate to others, and make decisions. Good emotional health is characterised by resilience, self-awareness, and the capacity to form fulfilling relationships.
Practices that support emotional well-being include maintaining social connections, practising gratitude, and seeking help when necessary. Professional mental health services can offer support for individuals experiencing persistent emotional difficulties.
Preventative Health Measures
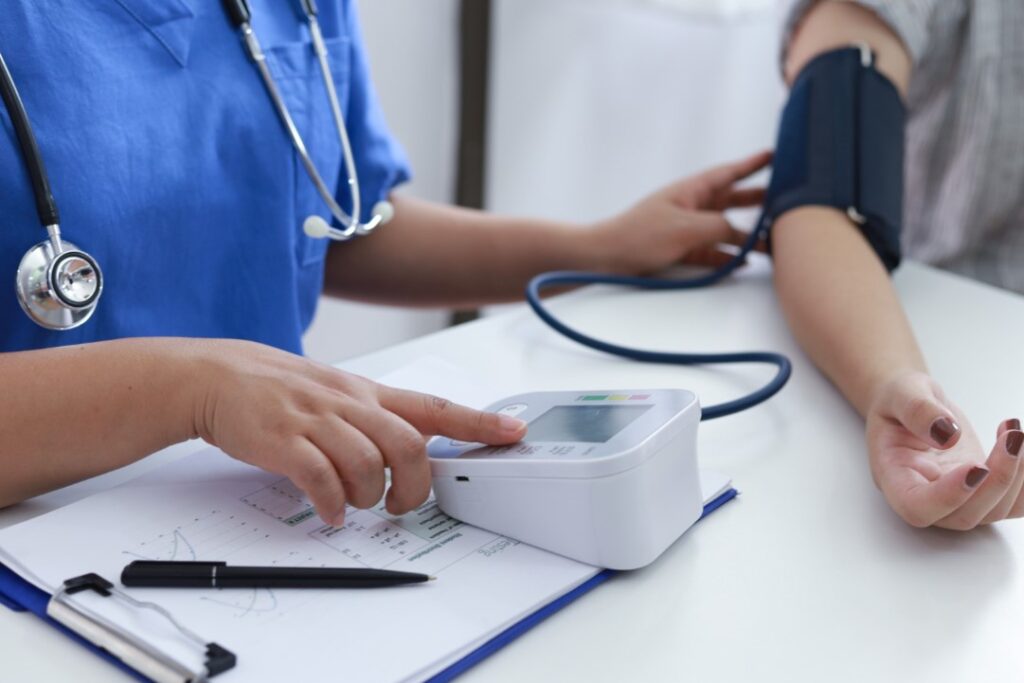
Regular Health Screenings
Preventive care is a key component of maintaining general health. Routine health screenings can identify risk factors and early signs of disease before symptoms develop. Common screenings include blood pressure measurement, cholesterol testing and cancer screenings appropriate for age and risk profile.
Engaging in regular check ups with a healthcare professional allows for tailored advice on lifestyle choices and management of existing conditions. Vaccinations are also an important preventative measure to protect against infectious diseases.
Hygiene and Safety Practices
Personal hygiene and safety practices are fundamental to reducing the risk of infection and injury. Hand washing, safe food handling and maintaining a clean living environment help prevent the spread of pathogens. Adhering to safety guidelines such as using seat belts, wearing appropriate protective equipment and observing workplace safety protocols further supports general health.
The Role of Public Information
Access to accurate, evidence-based information is vital in promoting healthy behaviours and preventing misinformation. Public health campaigns, scientific publications, and reputable news sources contribute to public understanding of health-related topics. Individuals benefit from critically assessing the quality of information and consulting qualified professionals when necessary.
Reliable updates on developments in health research, policy, and practice enable individuals to adapt their behaviours in ways that support long-term wellbeing. Engagement with credible sources and avoidance of unverified claims are essential components of responsible consumption of health information.
Building Sustainable Health Habits

Setting Realistic Goals
Establishing sustainable health habits involves setting realistic and achievable goals. Rather than attempting drastic changes, incremental adjustments in daily routines can lead to lasting improvements. For example, incorporating a short walk into a daily schedule or increasing fruit and vegetable intake gradually can be more manageable than large, immediate changes.
Monitoring progress and celebrating small successes can reinforce positive behaviours. It is also important to recognise that setbacks are a normal part of behaviour change and to approach them with patience and resilience.
Community and Support
Community environments influence individual health behaviours. Social networks, neighbourhood resources, and cultural norms can encourage or discourage healthy practices. Participation in community programmes, fitness groups, or educational workshops can provide motivation and support.
Healthcare professionals, educators, and policymakers all have roles in facilitating environments that promote general health. Collaborative efforts can help address barriers to healthy living and create opportunities for individuals to thrive.
Conclusion
General health is a multifaceted concept that integrates physical, mental, and social elements. By prioritising balanced nutrition, physical activity, sleep, and preventative care, individuals can support their overall wellbeing. Access to accurate information and engagement with supportive communities further enhance the capacity to make informed health choices. Consistent attention to these aspects contributes to resilience and a higher quality of life.

